Age: 67
Sex: Female
Indication: Chest pain, stroke-like symptoms
Save ("V")
Case #4
Findings
- Vascular findings
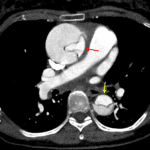
- Stanford type A aortic dissection extending from the aortic annulus at the level of the noncoronary aortic valve leaflet throughout the entire aorta and into the left common iliac artery
- Resultant aneurysmal dilation of the ascending aorta measuring up to 5.9 x 5.7 cm in cross-sectional diameter
- Moderate compression of the true lumen, which remains patent
- Dissection does not extend into the right or left main coronary arteries, though the false lumen does exert mass effect on the right and left coronary cusps
- Dissection extends into the brachiocephalic artery with resulting severe narrowing of the true lumen as well as occlusion of the origin of the right common carotid artery and severe narrowing at the origin of the right subclavian artery
- Dissection extends slightly into the origins of the left common carotid and left subclavian arteries without high-grade stenosis
- Linear intraluminal hypodensity in the proximal left common carotid artery
- Celiac trunk primarily arises from the true lumen with some contribution from the false lumen
- SMA, renal arteries, and IMA arise from the true lumen and are patent
- It is unclear whether the left internal iliac artery arises from the true or false lumen
- No hemopericardium or hemothorax
- Nonvascular findings
- Mild cardiomegaly
- Small hiatal hernia
- Mild centrilobular emphysema
- Mild widespread bronchial wall thickening
- Ill-defined area of groundglass opacification in the lingula
- Mild bilateral subpleural reticulation, suggesting mild fibrosis
- Scattered hypodense liver lesions, many of which are too small to characterize
- Cholelithiasis
- 2.7 cm enhancing solid mass arising from the upper pole of the right kidney
- Colonic diverticulosis
Diagnosis
- Aortic dissection
 Sample Report
Sample Report
Stanford type A aortic dissection originating at the noncoronary cusp of the aortic annulus, extends through the thoracic and abdominal aorta, and terminates in the left common iliac artery. Resultant aneurysmal dilation of the ascending aorta measuring up to 5.9 cm. The coronary arteries arise from the true lumen and are patent. No hemopericardium or hemothorax.
Dissection extends into the arch vessels with notable occlusion of the proximal right common carotid artery and severe narrowing of the brachiocephalic artery and right subclavian artery.
A linear intraluminal hypodensity in the proximal left common carotid artery may be artifactual, though a focal dissection at this location is not excluded. Recommend attention on followup imaging.
Mesenteric vessels arise from the true lumen and are patent, though there is a minor contribution to the celiac artery from the false lumen.
Enhancing solid right upper pole renal mass concerning for renal cell carcinoma.
Ill-defined area of groundglass opacification in the lingula, which may be infectious or inflammatory in etiology. Recommend attention on followup imaging to exclude malignancy.



 View shortcuts
View shortcuts Zoom/Pan
Zoom/Pan Full screen
Full screen Window/Level
Window/Level Expand/collapse
Expand/collapse Scroll
Scroll Save the case
Save the case Close case/tab
Close case/tab





 Previous series (if multiple)
Previous series (if multiple) Next series (if multiple)
Next series (if multiple)
