Age: 91
Sex: Female
Indication: Left-sided weakness
Save ("V")
Case #1
Findings
- Large area of restricted diffusion in the right MCA territory
- Associated T2/FLAIR hyperintensity and swelling with right cerebral sulcal effacement and 3 mm right-to-left midline shift
- Basal cisterns are patent
- Abnormal flow-related signal in the communicating segment of the right internal carotid artery and in the M1 segment of the right MCA
- Few small foci of susceptibility artifact in the right frontal lobe
- Confluent subcortical and periventricular white matter T2/FLAIR hyperintensity
- Remote lacunar infarcts in the pons
- Generalized cerebral volume loss
- Bilateral pseudophakia
Diagnosis
- Thrombotic stroke
 Sample Report
Sample Report
Large acute/early subacute right MCA territory infarct. Associated cytotoxic edema with resultant right cerebral sulcal effacement and 3 mm right-to-left midline shift. No evidence of herniation or hydrocephalus.
Few small foci of susceptibility artifact in the right frontal lobe may represent petechial hemorrhage, though there is no evidence of organized hemorrhagic conversion.
Abnormal flow-related signal in the communicating segment of the right internal carotid artery and in the M1 segment of the right MCA concerning for diminished/slow flow or occlusion. Recommend correlation with CTA or catheter angiography.
Confluent subcortical and periventricular white matter T2/FLAIR hyperintensity, which though nonspecific likely relates to chronic small vessel disease. Remote lacunar infarcts in the pons. Generalized cerebral volume loss.
Discussion
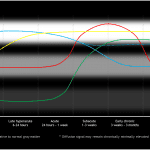
- MRI is much more sensitive than CT for the detection of early cerebral infarcts
- Abnormal signal first becomes apparent on diffusion/ADC, often present by mere minutes after the vascular occlusion occurs
- ADC signal normalizes more quickly (typically by 10 days) than diffusion signal because of T2 effects which may transiently or permanently keep diffusion signal mildly elevated
- T2/FLAIR signal abnormality lags somewhat, typically starting to become apparent 6-8 hours after the occlusion
- There are three types of enhancement that can be observed with strokes:
- Arterial enhancement (hours to days after stroke) – decreased arterial blood flow within the area of acute ischemia results in decreased flow-related signal loss. This increased intrinsic signal combined with the signal from administered contrast material makes these vessels appear more hyperintense than unaffected arteries
- Meningeal enhancement (1-7 days after stroke) – resulting from reactive hyperemia in the meninges overlying the infarct. This is the least commonly observed type of enhancement
- Parenchymal enhancement (1 week – 3 months) – resulting from breakdown of the blood-brain barrier. Parenchymal enhancement may occur earlier and more intensely in incomplete infarcts. If you are trying to determine if an enhancing lesion is an infarct vs neoplasm, repeating imaging in a few months can help differentiate the two
- Refer to the figure below for a graphical representation of the typical progression of MR signal in cerebral vascular accidents
📣 Feedback?
⌨️ Keyboard Shortcuts ("K")
Help | Terms | Privacy Policy | Cookie Policy
Medical Disclaimer | © 2024 CaseStacks LLC
Related Cases
References
- Allen LM, Hasso AN, Handwerker J, Farid H. Sequence-specific MR imaging findings that are useful in dating ischemic stroke. Radiographics 2012; 32: 1285-1297.
- . Evolution of MR contrast enhancement patterns during the first week after acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2001; 22(1): 103-111.


 View shortcuts
View shortcuts Zoom/Pan
Zoom/Pan Full screen
Full screen Window/Level
Window/Level Expand/collapse
Expand/collapse Scroll
Scroll Save the case
Save the case Close case/tab
Close case/tab





 Previous series (if multiple)
Previous series (if multiple) Next series (if multiple)
Next series (if multiple)
