Age: 35
Sex: Female
Indication: Trauma
Save ("V")
Case #2
Findings
Chest radiograph
- Left thoracostomy tube is positioned with tip overlying the left lung apex
- Small left apical pneumothorax
- Additional lucency along the medial aspect of the left hemidiaphragm may represent a small basilar pneumothorax
- Patchy opacities throughout the left greater than right lungs
- Mild left chest wall subcutaneous emphysema
CT
- Chest
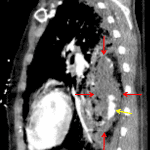
- Extensive left lower lobe pulmonary hemorrhage with a focal hematoma measuring 4.5 x 2.5 x 8 cm
- Within this hematoma are multiple hyperattenuating foci
- Surrounding areas of groundglass opacification in the left upper and lower lobes as well as in the posterior segment of the right upper lobe
- Small left hemopneumothorax with thoracostomy tube tip in the posterior left apex, possibly within the major fissure
- Mild biapical paraseptal emphysema, which decreases sensitivity for a trace pneumothorax on the right
- Left subclavian approach central venous catheter with tip at the superior cavoatrial junction
- Abdomen/Pelvis
- No acute findings
- Cholelithiasis
- MSK
- Partially imaged acute mildly displaced C6 vertebral fracture involving the left transverse process, pedicle, and lamina as well as the spinous process
- Acute mildly displaced and comminuted fracture of the left C7 pars interarticularis extending into the ipsilateral pedicle and lamina
- Acute minimally displaced fractures of the left T8-T10 transverse processes and possible nondisplaced fractures of the left T5-T7 transverse processes
- Acute fractures of the right anterior third through fifth, left anterior fourth through sixth, and left posterior seventh through ninth ribs with varying degrees of displacement
- Partially imaged fractures of the left ulna and radius and possibly trapezoid. Adjacent soft tissue gas in the forearm raises concern for open fracture
- Hyperattenuating areas and metallic debris amidst soft tissue stranding and hematoma in the anterior left upper arm
- Acute comminuted subtrochanteric right femoral fracture with apex posterior angulation. Right hip is located
- Multiple superior endplate compression deformities spanning T2-T4 and T8-T11 with minimal height loss and no bony retropulsion
- Intraosseous line in the posterior aspect of the right humeral head
Diagnosis
- Pulmonary laceration
 Sample Report
Sample Report
Extensive left pulmonary laceration with a focal intraparenchymal hematoma, predominantly involving the left lower lobe, and evidence of active internal bleeding.
Small left hemopneumothorax with apically directed left thoracostomy tube in place.
Findings concerning for active bleeding in the anterior left upper arm.
Acute fracture of the left fourth through ninth and right third through fifth ribs.
Incompletely imaged acute open fractures of the left radius and ulna and possibly of the trapezoid. Recommend correlation with dedicated radiographs of the forearm and wrist.
Acute comminuted subtrochanteric right femoral fracture without hip dislocation.
Multiple acute spinal fractures are noted, including: Partially imaged acute mildly displaced C6 vertebral fracture involving the left transverse process, pedicle, and lamina as well as the spinous process, acute mildly displaced and comminuted fracture of the left C7 pars interarticularis and adjacent posterior elements, acute minimally displaced fractures of the left T8-T10 transverse processes and possible nondisplaced fractures of the left T5-T7 transverse processes, and multiple superior endplate compression fractures from T2-T4 and T8-T11 with minimal height loss and no bony retropulsion.
Discussion
- Pulmonary laceration will often take a round/oval shape because the surrounding lung will pull away from the injury due to elastic recoil
- If this cavity fills with air, then it is called a pneumatocele, and if it fills with blood it is called a hematoma
- Unlike contusions, lacerations may take months or longer to resolve and are more likely to result in chronic scarring with focal architectural distortion
- Lacerations can result from several mechanisms including blunt injury compressive forces causing rupture of neighboring alveoli deep within the pulmonary parenchyma or superficial alveolar rupture from penetrating injury (e.g. knife or gunshot wound) or inwardly-displaced rib fracture
- Always look for active bleeding when you see a hematoma
- Many trauma protocols will only have delayed imaging of the abdomen and pelvis. It may be a good idea to request inclusion of the chest if you see extensive chest trauma on arterial phase images and are reading the study in real time
- This case is also a good example of tough corner findings


 View shortcuts
View shortcuts Zoom/Pan
Zoom/Pan Full screen
Full screen Window/Level
Window/Level Expand/collapse
Expand/collapse Scroll
Scroll Save the case
Save the case Close case/tab
Close case/tab





 Previous series (if multiple)
Previous series (if multiple) Next series (if multiple)
Next series (if multiple)
