Age: 15
Sex: Male
Indication: Neck injury, no fracture on radiographs
Save ("V")
Case #2
Findings
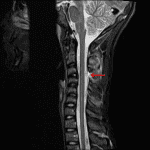
- Focal kyphosis with widening of the interspinous distance at C3-C4
- Perched right C3-C4 facet joint
- No abnormal marrow T2/STIR hyperintensity
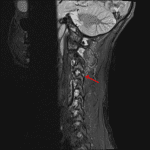
- T2/STIR hyperintensity in the interspinous ligaments at multiple levels, most pronounced at C2-C3, C3-C4, and C5-C6, and in the supraspinous ligament at the levels of C2-C3 and C3-C4
- T2/STIR hyperintensity in the right C3-C4 facet joint
- Severe thinning and possible focal discontinuity of the ligamentum flavum at the levels of C3-C4 and C4-C5
- Small posterior disc bulges at C3-C4 and C4-C5 result in partial effacement of the ventral CSF without significant spinal canal stenosis
- No abnormal spinal cord signal
- No significant epidural collection
- Normal flow-related signal loss in the carotid and vertebral arteries in the neck
Diagnosis
- Cervical spine ligamentous injury
 Sample Report
Sample Report
Flexion distraction injury at C3-C4 with traumatic kyphosis, widening of the interspinous distance, and perched right C3-C4 facet. No marrow edema to suggest acute fracture, though CT should be considered for further evaluation given that only radiographs were obtained previously.
Findings concerning for severe thinning and possible focal disruption of the ligamentum flavum and C3-C4 and C4-C5, right C3-C4 facet capsular injury, multilevel interspinous ligament injury, most pronounced at C2-C3, C3-C4, and C5-C6, and supraspinous ligament injury at C2-C3 and C3-C4.
Likely traumatic disc bulges at C3-C4 and C4-C5, which partially efface the ventral CSF without significant spinal canal stenosis. No abnormal cord signal.
Discussion
- Ligament, disc, and cord injuries as well as extramedullary collections are much better assessed on MRI than on CT
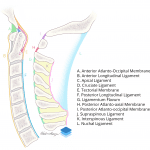
- Below the craniocervical junction (i.e. below the level of C2), the important ligaments to assess are the:
- Anterior longitudinal ligament
- Posterior longitudinal ligament
- Ligamentum flavum
- Interspinous ligaments
- Supraspinous ligament
- Hyperflexion injuries result in narrowing of the anterior column and widening of the posterior column, as shown in this case with kyphotic deformity and widening of the interspinous distance at the involved level
- Important blind spots on spine MRI that are important to double check include:
- Vessels, particularly the vertebral arteries on cervical MRI
- Discs – while disc herniations are often written off as chronic degenerative findings, they can be traumatic and are particularly suspicious in young patients who do not have background degenerative changes
- Facet joints – these are easier to overlook on sagittal images since they are not midline structures
- Some pitfalls of MRI in evaluation of spine trauma include:
- Marrow edema is often subtle or absent acutely, so do not trust MRI to rule out acute fracture
- Normal vessels run in the interspinous intervals, which may appear hyperintense on STIR. These are usually more sharply demarcated than edema associated with ligamentous injury


 View shortcuts
View shortcuts Zoom/Pan
Zoom/Pan Full screen
Full screen Window/Level
Window/Level Expand/collapse
Expand/collapse Scroll
Scroll Save the case
Save the case Close case/tab
Close case/tab





 Previous series (if multiple)
Previous series (if multiple) Next series (if multiple)
Next series (if multiple)
